People with enduring hardships caused by the disease known as glaucoma can rejoice as there has been a major break through. Huge strides have been made in creating cure for this before uncurable disease. This disease affecting 80 million people in the US alone leading to blindness. New research from top world universities have a new drug that could reverse the effects of gluacoma.
These fatty molecules, lipoxins, known for their inflammation-regulating potential, were shown to reduce and stops degeneration of cells in mice with glaucoma. Retinal ganglion cells connect the retina to the photoreceptors in the eye, an essential connection for retaining full functioning of the eye. These anti-inflammatory lipoxins, secreted from the most common type of glial cell in the brain, were shown in this investigation to play a role in neuroprotection.
Astrocytes are commonly thought to injure ganglion cells by releasing stress signals. Though, Flanagan’s research has discovered unexpectedly that “astrocytes that are triggered by injury actually turns off signals that stop nerve damage.” Two variants of lipoxins were discovered to be secreted from resting astrocytes in eyeball and at the head of the nerve. Considering that these astrocytes weren’t encountering any stress signals when releasing these lipoxins, the researchers thought that these lipoxins may have a role in enhancing neuroprotection and reducing optic nerve damage.
This discovery led the researchers to isolate the A4 and B4 variants of Lipoxin and administer them to rodents with glaucoma and neurodegeneration that had been recognized eight weeks earlier. At 16 weeks the initial start of the disease, and 8 weeks after the administration of the two variants, the rats’ ganglion cell functioning was shown to significantly similar to the functioning seen eight weeks earlier, showing that the lipoxin had reduced, or completely stopped the nerve degeneration caused by glaucoma. In particular, the B4 variant was shown to stop the cells’ degeneration. Currently, there are no drugs or natural molecules known to show this potential in the reversal or stagnation of cell death.
Glaucoma is one of many well-known disorders like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s that are characterized by their degradative influence over the central nervous system. The pharmaceutical industry has sought remedy for these diseases for decades. Only recently had the industry attempted to use lipoxins to reduce inflammation, but never as a neuroprotective solution. With the patents for lipoxin A4 and B4, the study authors hope to enter human trials promptly.
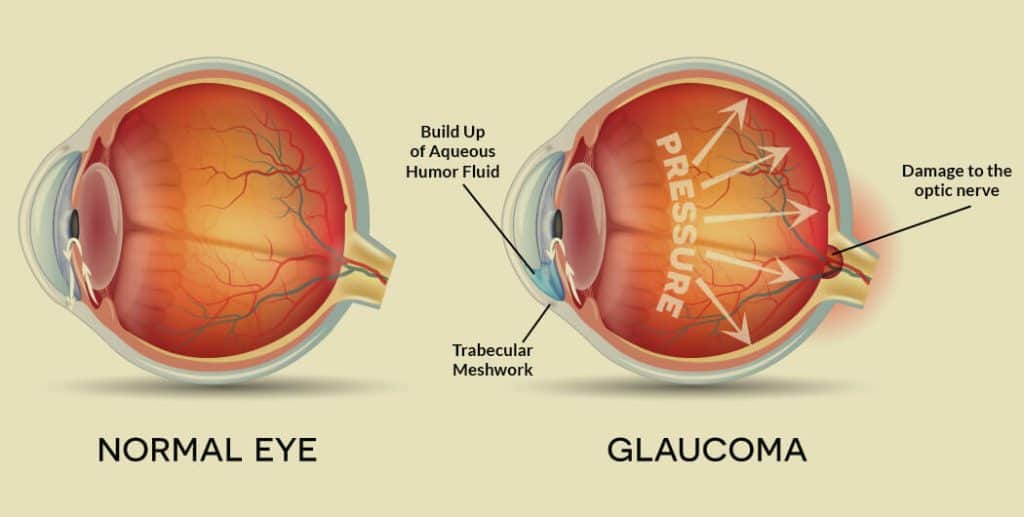
Currently, patients with glaucoma have only one option for treatment: a reduction in ocular pressure by the removal of backed-up fluid. Though this procedure helps in the short term with the progression of the disease and discomfort, the neurodegeneration is unavoidable and irreversible.
For this reason, the potential to stagnate or reverse the deterioration of the optic nerve is groundbreaking for glaucoma and other nerve-related diseases.
This impressive research, there are other groups making waves in the glaucoma space. Should a cure not play out in the near future, a group has recently published results from the largest genetic study ever done with glaucoma patients, involving 134,000 people. The study found 53 genetic markers that directly increase the risk for glaucoma, especially the advanced form of the disease that leads to total blindness.
Despite there being no cure, these predictive genetic markers may help patients take precautionary steps to remove fluid buildup in the eye to delay the otherwise rapid onset of the disease. This would be the first predictive test for glaucoma. With periodic screenings and the advent of personal genetic screenings led by companies like 23andMe and others, there is a chance in the near future that the common name for the disease, the “sneak thief of sight,” won’t be quite as accurate.
MIT along with several collaborators recently published in Nature, one of the most prestigious science journals, a fascinating finding that relabels glaucoma as a potential autoimmune disease. They found that raised intraocular pressure was sufficient to allow T-cell infiltration, a cell of the body’s immune system, into the optic nerve of the eye. Upon entering the eye, the T cells were found to be attacking heat-shock proteins on the optic nerve of mice with a specific type of bacteria found in the eye. In glaucomic mice, these bacterial populations were up-to five-times higher than those without glaucoma. When the bacteria were removed in future trials, the T cell infiltration of the eye did not lead to degeneration of the optic nerve.
These results reveal a sequence of the disease that has never before been so clearly laid out. This finding hints that the body may be able to be trained not to attack itself using a sort of immunotherapy or other immune normalization.
source – http://globalgadgetnews.com/